Comptt
(Set - II Outside Delhi )
Section A
Q. 1. A wire of resistance 6  is bent to form a closed square. What is the resistance across a diagonal of the square? 1
is bent to form a closed square. What is the resistance across a diagonal of the square? 1
 is bent to form a closed square. What is the resistance across a diagonal of the square? 1
is bent to form a closed square. What is the resistance across a diagonal of the square? 1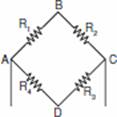
AB = BC = CD = AD
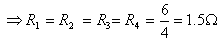
Resistance across AC is given by R
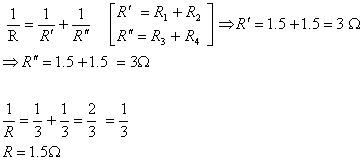
Q. 2. What is the shape of the graph between V and I, where V is the potential difference between the ends of an ohmic resistor and I is the current flowing through it? 1
Ans. The graph between V and I is a straight line passing through the origin.

Q. 3. State the first limitation of Mendeleev’s periodic table. 1
Ans. Limitation of Mendeleev’s periodic table:
- The position of isotopes could not be explained as isotopes are the atoms of the same element having similar chemical properties but different atomic masses.
Q. 4. Draw the structure of ethanol molecule.
Ans. Ethanol C2H5OH
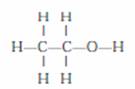
Q. 5. A wire of resistance 20 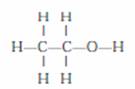
 is bent to form a closed square. What is the resistance across a diagonal of the square?
is bent to form a closed square. What is the resistance across a diagonal of the square? 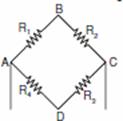
Ans. Total resistance of the wire = 20 
AB = BC = CD = AD
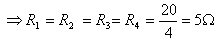
Resistance across AC is given by R
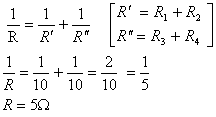
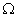
AB = BC = CD = AD
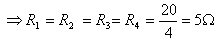
Resistance across AC is given by R
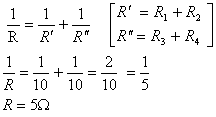
Q. 6. Name the gas usually liberated when a dilute acid reacts with a metal. What happens when a burning candle is brought near this gas? 1
Ans. When a dilute acid reacts with a metal, usually hydrogen gas is liberated. When a burning candle is brought near this gas, it burns with a ‘pop’ sound.
Q. 7. What is the basis of Mendeleev’s periodic table? Write two achievements of Mendeleev’s periodic table. 2
Ans. Basis.
Achievements of Mendeleev’s periodic table.
Achievements of Mendeleev’s periodic table.
Q. 8. State Mendeleev’s periodic law. Write two achievements of Mendeleev’s periodic table. 2
Ans.
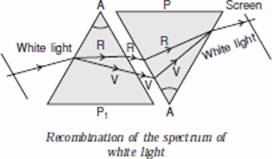
Q. 9. What is meant by spectrum? How can we recombine the components of white light after a prism has separated them? 2
Ans • When a beam of white light is passed through a glass prism, a band of seven colours is formed on a white screen. This band of seven colours is called spectrum of white light.
• Newton showed that the seven coloured lights of the spectrum can be recombined to give back white light.
• First he tried to split the colours of the spectrum of white light using a prism.
• He then placed a second identical prism in an inverted position with respect to the first prism. This allowed all the colours of the spectrum to pass through the second prism. He found a beam of white light emerging from the other side of the second prism.
• Newton showed that the seven coloured lights of the spectrum can be recombined to give back white light.
• First he tried to split the colours of the spectrum of white light using a prism.
• He then placed a second identical prism in an inverted position with respect to the first prism. This allowed all the colours of the spectrum to pass through the second prism. He found a beam of white light emerging from the other side of the second prism.
Q.10. Give reasons for the following. 2
(i) The sun appears reddish at sunrise or sunset.
(ii) The sky appears dark instead of blue to an astronaut.
(i) The sun appears reddish at sunrise or sunset.
(ii) The sky appears dark instead of blue to an astronaut.
Ans. (i) The Sun at the time of sunrise and sunset is more near the horizon, and near the horizon most of the blue light of shorter wavelengths is scattered away by the particles and gases of the atmosphere. Light from the Sun near the horizon passes through thick layers of air and larger distance in the Earth’s atmosphere before reaching our eyes. Therefore, the light that reaches our eyes is of longer wavelength that gives rise to the reddish appearance of the sun.
(ii) The sky appears dark instead of blue to an astronaut because there is no atmosphere containing air in the outer space to scatter sunlight.
(ii) The sky appears dark instead of blue to an astronaut because there is no atmosphere containing air in the outer space to scatter sunlight.
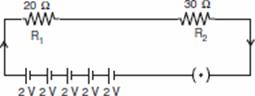
Q. 11. Draw a schematic diagram of an electric circuit consisting of a battery of five 2 V cells, a 20  resistor, a 30
resistor, a 30  resistor, a plug key, all connected in series. Calculate the value of current flowing through the 20
resistor, a plug key, all connected in series. Calculate the value of current flowing through the 20 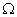 resistor and the power consumed by the 30
resistor and the power consumed by the 30 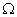 resistor. 3
resistor. 3
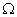 resistor, a 30
resistor, a 30 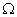 resistor, a plug key, all connected in series. Calculate the value of current flowing through the 20
resistor, a plug key, all connected in series. Calculate the value of current flowing through the 20 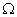 resistor and the power consumed by the 30
resistor and the power consumed by the 30 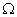 resistor. 3
resistor. 3Ans. R1 = 20 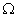 R2 = 30
R2 = 30 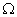
Resultant resistance, R = R1 + R2 = 20 + 30 = 50
Total potential difference, V = 5 X2 = 10 volts
Current, I = ?
By Ohm’s Law,
V = I R
I =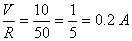
Since current remains constant in a series.
I = I1 + I2
∴ The current flowing through
20 resistor is also 0·2 A.
resistor is also 0·2 A.
Power consumed by 30 resistor,
resistor,
P2 = V2I2
I2 = 0·2 A R2 = 30 V2 = ?
V2 = ?
V2 = I2R2 = 0·2 X = 6 volts P2 = 6 X 0·2 = 1·2 W
 R2 = 30
R2 = 30 
Resultant resistance, R = R1 + R2 = 20 + 30 = 50
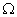
Total potential difference, V = 5 X2 = 10 volts
Current, I = ?
By Ohm’s Law,
V = I R
I =
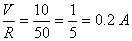
Since current remains constant in a series.
I = I1 + I2
∴ The current flowing through
20
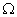 resistor is also 0·2 A.
resistor is also 0·2 A.Power consumed by 30
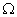 resistor,
resistor,P2 = V2I2
I2 = 0·2 A R2 = 30
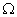 V2 = ?
V2 = ?V2 = I2R2 = 0·2 X = 6 volts P2 = 6 X 0·2 = 1·2 W

Q. 12. What is ethanol? Draw the structure of ethanol molecule. How does ethanol behave with the following :
(a) Sodium
(b) Excess of conc. sulphuric acid at 443 K
Write chemical equation for each reaction. 3
Ans.
(a) Sodium
(b) Excess of conc. sulphuric acid at 443 K
Write chemical equation for each reaction. 3
Ans.
- Ethanol is the second member of the homologous series of alcohol. It’s formula is C2H5OH. It is the most widely used alcohol. It’s common name is ethyl alcohol.
- Structure formula
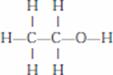
- Ethanol reacts with sodium to form sodium ethoxide and hydrogen gas
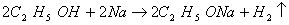
- When ethanol is heated with excess of conc. sulphuric acid at 443 K, it gets dehydrated to form ethene
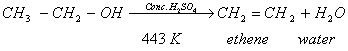
Q. 13. What is ethanoic acid? Write the formula of the functional group present in this acid. What special name is given to its 5–8% solution in water? How does ethanoic acid react with sodium carbonate? Write the chemical equation of the reaction and common name of the salt produced. 3
Ans.
- Ethanoic acid is the second member of the homologous series of carboxylic acids. The formula of ethanoic acid is CH3COOH and the functional group present in it is carboxylic acid i.e. —COOH.
- Its 5 – 8% solution in water is called vinegar.
- When ethanoic acid reacts with sodium carbonate, carbon dioxide gas is evolved along with the formation of salt and water. 2CH3COOH + Na2CO3→ 2CH3COONa + CO2 + H2O
Ethanoic acid Sodium carbonate Sodium ethanoate
The common name of the salt produced is Sodium acetate.
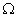 resistor, a 20
resistor, a 20 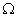 resistor, a plug key, all connected in series. Calculate the value of current flowing through the 10
resistor, a plug key, all connected in series. Calculate the value of current flowing through the 10 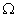 resistor and the power consumed by the 20
resistor and the power consumed by the 20 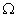 resistor.
resistor.Ans.
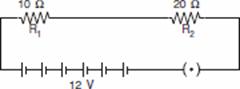

R1 = 10  and R2 = 20
and R2 = 20 
Resultant resistance, R = R1 + R2
R = 10 + 20 = 30
Total voltage = 12 volts
Total current, I = ?
V = I R
I =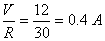
 and R2 = 20
and R2 = 20 
Resultant resistance, R = R1 + R2
R = 10 + 20 = 30
Total voltage = 12 volts
Total current, I = ?
V = I R
I =
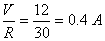
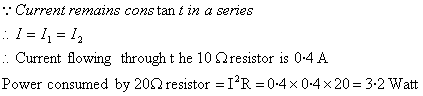
Q.15. (a) What is a reactivity series? Describe an activity to develop a reactivity series.
(b) Write two physical and two chemical properties of non-metals. 5
(b) Write two physical and two chemical properties of non-metals. 5
Ans. (a) The arrangement of metals in a vertical column in the order of their decreasing reactivities is called reactivity series of metals.
Activity:
Activity:
- Some metals are chemically very reactive whereas others are less reactive e.g. potassium and sodium react vigorously with cold water so these are very-very reactive metals.
- Calcium reacts with cold water but not vigorously.
- Magnesium does not react with cold water but reacts with hot water.
- Aluminium and zinc react with steam so these metals are less reactive than Magnesium.
- Iron does not react with steam but red hot iron reacts with steam so iron is less reactive than aluminium and zinc.
- Whereas copper and silver do not react with water at all. So they are very-very less reactive metals.
So on the basis of reaction of metals with water, we can arrange.
K > Na > Ca > Mg > Al > Zn > Fe > Cu > Ag.
(b) Two physical properties of non-metals
• Non-metals are neither malleable nor ductile.
• Non-metals do not conduct heat and electricity.
Two chemial properties of non-metals
• Reaction of non-metals with oxygen
Non-metals react with oxygen to form acidic oxides or neutral oxides.
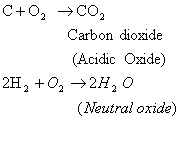
• Reaction of non-metals with chlorine
Non-metals react with chlorine to form covalent chlorides which are non-electrolytes.
• Non-metals are neither malleable nor ductile.
• Non-metals do not conduct heat and electricity.
Two chemial properties of non-metals
• Reaction of non-metals with oxygen
Non-metals react with oxygen to form acidic oxides or neutral oxides.
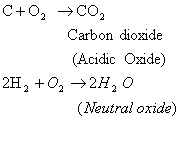
• Reaction of non-metals with chlorine
Non-metals react with chlorine to form covalent chlorides which are non-electrolytes.
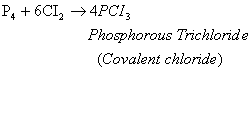
Or
(a) What is meant by corrosion? Name any two methods used for the prevention of corrosion.
(b) Suppose you have to extract metal M from its enriched sulphide ore. If M is in the middle of the reactivity series write various steps used in extracting this metal. 5
(b) Suppose you have to extract metal M from its enriched sulphide ore. If M is in the middle of the reactivity series write various steps used in extracting this metal. 5
Ans. (a) The eating up of metals by the action of air, moisture or a chemical (such as an acid) on their surface is called corrosion.
Prevention of corrosion:
(i) Corrosion or rusting of iron can be prevented by painting, oiling, greasing, galvanising, crome plating, anodising.
(ii) Corrosion of metals can also be prevented by alloying them with suitable metals or non metals in a required proportion.
Prevention of corrosion:
(i) Corrosion or rusting of iron can be prevented by painting, oiling, greasing, galvanising, crome plating, anodising.
(ii) Corrosion of metals can also be prevented by alloying them with suitable metals or non metals in a required proportion.
(b) M is in the middle of the reactivity series. Various steps which can be used to extract it from its enriched sulphide ore are as follows:
(i) Roasting: The enriched sulphide ore of ‘M’ is strongly heated in the presence of air to convert it into metal oxide.
(ii) Reduction: The metal oxides obtained by roasting is converted to free metal ‘M’ by reducing agents like carbon, aluminium, sodium or calcium.
(iii) Refining: The metal ‘M’ obtained by reduction contains some impurities. Thus this impure metal ‘M’ undergoes purification. The process of purifying impure metal is called refining. The most widely used method for refining is electrolytic refining.
(i) Roasting: The enriched sulphide ore of ‘M’ is strongly heated in the presence of air to convert it into metal oxide.
(ii) Reduction: The metal oxides obtained by roasting is converted to free metal ‘M’ by reducing agents like carbon, aluminium, sodium or calcium.
(iii) Refining: The metal ‘M’ obtained by reduction contains some impurities. Thus this impure metal ‘M’ undergoes purification. The process of purifying impure metal is called refining. The most widely used method for refining is electrolytic refining.
Q.16. (a) State Fleming’s left-hand rule. Apply this rule and find the direction of force acting on the electron that enters a magnetic field at right angles to it as shown in the figure. 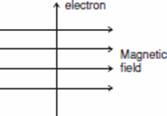
(b) When is an electric circuit said to be overloaded? State two measures to avoid it. What name is given to a situation in which the live and the neutral wires accidentally come in contact? State the role a safety device may play in this situation.

(b) When is an electric circuit said to be overloaded? State two measures to avoid it. What name is given to a situation in which the live and the neutral wires accidentally come in contact? State the role a safety device may play in this situation.
Ans. (a) According to Fleming’s Left Hand Rule: Hold the forefinger, the centre finger and the thumb of your left hand at right angles to one another. Adjust your hand in such a way that the forefinger points in
the direction of magnetic field and the centre finger points in the direction of current, then the direction in which thumb points, gives the direction of force acting on the conductor.
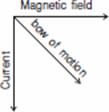
• In the given example the direction of force acting on the electron is out of the page because the direction of force is perpendicular to the direction of magnetic field and current given by Fleming’s Left Hand Rule. The direction of current is taken opposite to the direction of motion of electrons i.e. in this case in the downward (south) direction and direction of magnetic field is towards east. Therefore the force is directed out of the page.
the direction of magnetic field and the centre finger points in the direction of current, then the direction in which thumb points, gives the direction of force acting on the conductor.

• In the given example the direction of force acting on the electron is out of the page because the direction of force is perpendicular to the direction of magnetic field and current given by Fleming’s Left Hand Rule. The direction of current is taken opposite to the direction of motion of electrons i.e. in this case in the downward (south) direction and direction of magnetic field is towards east. Therefore the force is directed out of the page.
(b) Overloading and measures to avoid it:
• When the live and the neutral wires accidentally come in contact, this situation is known as short-circuiting.
• A fuse is the most important safety device. A fuse is a safety device having short length of a thin, tin-plated copper wire having low melting point, which melts and breaks if the current exceeds a safe value. A fuse is used for protecting the circuits and electric appliances from damage at the time of overloading or shortcircuiting of the circuits.
• When the live and the neutral wires accidentally come in contact, this situation is known as short-circuiting.
• A fuse is the most important safety device. A fuse is a safety device having short length of a thin, tin-plated copper wire having low melting point, which melts and breaks if the current exceeds a safe value. A fuse is used for protecting the circuits and electric appliances from damage at the time of overloading or shortcircuiting of the circuits.
Or
(a) With the help of a diagram describe in brief an activity to show that a magnetic field is produced by a current carrying circular coil. Draw a diagram to show the pattern of the magnetic field lines in this case.
(b) State the function of the earth wire in domestic electric circuits. Why is the metallic body of an electric appliance connected to the earth wire? Write the colour used for insulation of the earth wire.
Ans. (a) Magnetic field produced by a current carrying circular coil.
(i) A rectangular card board having holes is taken and a circular coil having large number of turns is
inserted in the cardboard. The coil should be inserted in the cardboard in such a manner that the
coil is normal to the plane of the cardboard.
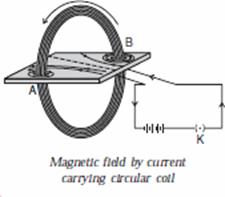
(i) A rectangular card board having holes is taken and a circular coil having large number of turns is
inserted in the cardboard. The coil should be inserted in the cardboard in such a manner that the
coil is normal to the plane of the cardboard.

(ii) The ends of the coil are connected in series with a battery, a key and a rheostat.
(iii) Then iron filings are sprinkled uniformly on the cardboard.
(iv) Now the key is plugged.
(v) On tapping the cardboard gently, the circular magnetic field lines near the current carrying loop are observed. On moving away from the circular loop, the concentric circles representing magnetic field lines become bigger and bigger. At the centre of the circular loop, the magnetic field lines are straight.
(b) The earth wire is used as a safety measure for electrical appliances having a metallic body. e.g., electric press, toaster, table fan, refrigerator etc. The earth wire, which has insulation of green colour
is usually connected to a metal plate dug deep inside the earth near the house. The leaked current from the appliance passes directly to the earth through the earth wire. Actually a very heavy current flows
through the earth wire and the fuse of household wiring melts and cuts off the power supply.
The appliance having metallic body is connected to the earth wire as it provides a low-resistance conducting path for the current. Thus it ensures that any leakage of current to the metallic body of the
appliance keeps its potential to that of the earth, and the user does not get a severe electric shock.
is usually connected to a metal plate dug deep inside the earth near the house. The leaked current from the appliance passes directly to the earth through the earth wire. Actually a very heavy current flows
through the earth wire and the fuse of household wiring melts and cuts off the power supply.
The appliance having metallic body is connected to the earth wire as it provides a low-resistance conducting path for the current. Thus it ensures that any leakage of current to the metallic body of the
appliance keeps its potential to that of the earth, and the user does not get a severe electric shock.
Section B
Q. 17. Why are coal and petroleum considered to be non-renewable sources of energy? 1
Ans. Coal and petroleum are considered to be non-renewable sources of energy because these fuels were formed over millions of years and there are only limited reserves and if all the coal and petroleum gets exhausted, these can not be produced quickly in nature.
Q. 18. Name the main hormone secreted by thyroid gland and state its one function. 1
Ans. • Thyroxine
• It controls the rate of metabolism of carbohydrates, fats and proteins in the body.
• It controls the rate of metabolism of carbohydrates, fats and proteins in the body.
Q. 19. What is meant by renewable natural resources? 1
Ans. The sources of energy which are being produced continuously by nature and are inexhaustible are called renewable sources of energy. For example: Hydel energy, Wind energy, Solar energy, Biomass energy etc.
Q. 20. Write the name and functions of any two parts of the human hind brain. 2
Ans. Pons, Cerebellum and Medulla are the parts of hind brain
• The pons take part in regulating respiration.
• Cerebellum helps to maintain posture and balance of the body.
• The pons take part in regulating respiration.
• Cerebellum helps to maintain posture and balance of the body.
Q. 21. What is reproduction? What are its two types? Which one of the two confers new characteristics on the offsprings and how? 2.
Ans. The production of new organisms from the existing organisms of the same species is known as reproduction.
There are two main methods of reproduction:
(i) asexual reproduction
(ii) sexual reproduction
The sexual reproduction confers new characteristics on the offsprings because the offspring receives some genes from the mother and some from the father and the mix of genes of mother and father in various different combinations causes genetic variation.
There are two main methods of reproduction:
(i) asexual reproduction
(ii) sexual reproduction
The sexual reproduction confers new characteristics on the offsprings because the offspring receives some genes from the mother and some from the father and the mix of genes of mother and father in various different combinations causes genetic variation.
Q. 22. State two problems caused by the non-biodegradable waste that we generate in our daily life. 2
Ans. Problems caused by the non-biodegradable waste:
(i) Non-biodegradable wastes cannot be made less toxic easily and hence they are major pollutants of the environment.
(ii) Non-biodegradable waste can be passed along the food chain from crops to man and other animals and harm them.
(i) Non-biodegradable wastes cannot be made less toxic easily and hence they are major pollutants of the environment.
(ii) Non-biodegradable waste can be passed along the food chain from crops to man and other animals and harm them.
Q. 23. Name the hormones secreted by testis and ovary. Write one function each of these hormones. 2
Ans. Testis: hormones–testosterone
• Its function is to control the development of male sex organs and male features.
• Its function is to control the development of male sex organs and male features.
Ovaries: hormones–oestrogen and progesterone.
• Oestrogen controls the development of female sex organs and female features.
• Progesterone controls the uterus and changes in menstrual cycle.
• Oestrogen controls the development of female sex organs and female features.
• Progesterone controls the uterus and changes in menstrual cycle.
Q. 24. What is binary fission? Draw a diagram to show binary fission in Amoeba. 2
Ans. Binary fission:
Q. 25. The human beings who look so different from each other in terms of colour, size and looks are said to belong to the same species. Why? Justify your answer. 3
Ans. The human beings who look so different from each other in terms of colour, size and looks are said to belong to the same species because the process of reproduction can occur between them. These differences are known as variations, i.e. the occurrence of differences among the individuals of a species. Although all human beings look different, they have the same number of chromosomes. A large number of variations occur in sexual reproduction because two parents are involved in the process and result in the birth of human beings of different colour, size and looks.Q. 26. What is meant by sustainable management? The environmentalists are insisting upon sustainable natural resources management”. State its four advantages. 3
Ans. The development which meets the current basic human needs and also preserves the resources for the needs of future generations is called sustainable management.
A system of controlling the use of natural resources in such a way as to avoid their wastage and to use them in the most effective way is called sustainable management.
A system of controlling the use of natural resources in such a way as to avoid their wastage and to use them in the most effective way is called sustainable management.
Advantages:
(i) The resources of the earth are limited. Proper management of these natural resources can ensure that these are used judiciously so that they fulfil the needs of the present generation and also last for the
generations to come.
(ii) The proper management of natural resources takes into consideration long-term perspective and prevents their exploitation to the hilt for short term gains.
(iii) Proper management can ensure equitable distribution of natural resources so that all the people can be benefitted.
(iv) Proper management will take into consideration the damage caused to the environment during the extraction or use of the natural resources and find ways and means to minimize the damage.
(i) The resources of the earth are limited. Proper management of these natural resources can ensure that these are used judiciously so that they fulfil the needs of the present generation and also last for the
generations to come.
(ii) The proper management of natural resources takes into consideration long-term perspective and prevents their exploitation to the hilt for short term gains.
(iii) Proper management can ensure equitable distribution of natural resources so that all the people can be benefitted.
(iv) Proper management will take into consideration the damage caused to the environment during the extraction or use of the natural resources and find ways and means to minimize the damage.
Q.27. (a) Draw a diagram to show the human alimentary canal and label on it the following :
Gall bladder, stomach Name the longest part of the alimentary canal.
(b) Why is it necessary to separate oxygenated and deoxygenated blood in mammals and birds? 5
Gall bladder, stomach Name the longest part of the alimentary canal.
(b) Why is it necessary to separate oxygenated and deoxygenated blood in mammals and birds? 5
Ans. (a) Human alimentary canal.
Longest part of the alimetary canal is small intestine (about 7 m long).
(b) Such separation of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood is necessary for highly efficient supply of oxygen to the body of birds and mammals which have high energy needs and constantly need energy
to maintain their body temperature.
Longest part of the alimetary canal is small intestine (about 7 m long).
(b) Such separation of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood is necessary for highly efficient supply of oxygen to the body of birds and mammals which have high energy needs and constantly need energy
to maintain their body temperature.
Or
(a) Draw a diagram to show excretory system in human beings and
label on it the following:
Aorta, Vena Cava
Name the excretory unit of kidney.
label on it the following:
Aorta, Vena Cava
Name the excretory unit of kidney.
(b) Differentiate between aerobic respiration and anaerobic respiration. After vigorous exercise, athletes and players generally experience cramps in their leg muscles. Why? 5
Ans. (a) Excretory System in human beings.
Nephron is the excretory unit of kidney.
Nephron is the excretory unit of kidney.
(b) Difference between aerobic respiration and anaerobic respiration. After vigorous exercise, athletes and players generally experience cramps in their leg muscles because anaerobic respiration takes place in the muscles during vigorous physical exercise. Oxygen gets used up faster in the muscle cells than that can be supplied by the blood. Anaerobic respiration produces lactic acid with release of a small amount of energy. The sudden build up of lactic acid in the muscles causes muscular cramps.
No comments:
Post a Comment