Comptt
Set- II - (Delhi)
Section A
Q. 1.Two resistors of 20 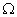 and 30
and 30 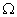 are connected in series to a battery of 4·5 V. How do the values of electric current passing through them compare?1
are connected in series to a battery of 4·5 V. How do the values of electric current passing through them compare?1
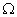 and 30
and 30 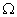 are connected in series to a battery of 4·5 V. How do the values of electric current passing through them compare?1
are connected in series to a battery of 4·5 V. How do the values of electric current passing through them compare?1Q. 2. Name the carbon compound which on heating with excess of concentrated sulphuric acid at 443 K gives ethene. 1
Ans. Ethanol on heating with excess of concentrated sulphuric acid at 443 K gives ethene.
Q. 3. Redraw the diagram given in your answer book and show the direction of the light ray after reflection from the mirror.
Ans
Q. 4. What is meant by a saturated hydrocarbon? 1
Ans. A saturated hydrocarbon is a hydrocarbon in which the carbon atoms are connected by only a single bond.
Q. 5. Chlorine, bromine and iodine form a Dobereiner’s triad. The atomic masses of chlorine and iodine are 35·5 and 126·9 respectively. Predict the atomic mass of bromine. 1
Ans.
Element of the triad | Symbol | Atomic masses |
1. Chlorine | Cl | 35·5 |
2. Bromine | Br | ? |
3. Iodine | I | 126·9 |
According to Dobereiner’s triad, the atomic mass of bromine is the arithmetic mean of Cl and I.
Q. 6. Write an expression for the heat produced H in time t in a heater of resistance R which is carrying a current I.
Ans. Heat produced, H = I2 x R x t joules
Activity :
(i) About 2 g of silver chloride is taken in a china dish. It is white in colour.
(ii) This china dish is placed in sunlight for some time.
(iii) It will be observed that white silver chloride turns grey due to formation of silver metal. This is a decomposition reaction.
(i) About 2 g of silver chloride is taken in a china dish. It is white in colour.
(ii) This china dish is placed in sunlight for some time.
(iii) It will be observed that white silver chloride turns grey due to formation of silver metal. This is a decomposition reaction.
Q. 8. Describe an activity to demonstrate what is observed when solutions of sodium sulphate and barium chloride are mixed together in a test tube. State the type of chemical reaction that takes place. 2
Ans. Activity when solutions of sodium sulphate and barium chloride are mixed:
(i) About 3 ml solution of sodium sulphate is taken in a test tube.
(ii) In another test tube, 3 ml of barium chloride solution is taken.
(iii) When solutions of sodium sulphate and barium chloride are mixed, a white precipitate of barium sulphate is formed at once.
(i) About 3 ml solution of sodium sulphate is taken in a test tube.
(ii) In another test tube, 3 ml of barium chloride solution is taken.
(iii) When solutions of sodium sulphate and barium chloride are mixed, a white precipitate of barium sulphate is formed at once.
Q. 9. The stars appear to twinkle while planets do not. Why? 2
Ans. The stars appear very-very small as they are far away so stars can be considered to be point sources of light. The continuously changing atmosphere causes variations in the light coming from the point sized stars due to refraction and thus the stars appear to be twinkling. On the other hand, the planets appear to be quite big as they are much nearer to the earth. So a planet can be considered to be a collection of a very large number of point sources of light. The dimming effect produced by some of the point sources of light in one part of the planet is nullified by the brighter effect produced by the point sources of light in its other part. Thus the brightness of a planet always remains the same and hence it does not appear to twinkle.
Q. 10. Why does the sky look blue on a clear sunny day? Explain. 2
Ans. See Q.18 (S.A.T), Chapter 11.
Q. 11. Draw a circuit diagram to show an electric lamp of resistance 60 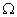 and a resistor of 12
and a resistor of 12 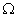 connected in series with a battery of 12 V. Calculate.
connected in series with a battery of 12 V. Calculate.
(a) total resistance in the circuit
(b) current flowing through the circuit
(c) potential difference separately across the lamp and the resistor. 3
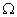 and a resistor of 12
and a resistor of 12 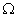 connected in series with a battery of 12 V. Calculate.
connected in series with a battery of 12 V. Calculate.(a) total resistance in the circuit
(b) current flowing through the circuit
(c) potential difference separately across the lamp and the resistor. 3
Q. 12. Soap does not work well with hard water. Name the class of compounds which can be used as cleansing agents in place of soap. Write the name of one such compound. Explain in brief the echanism of its cleansing action when used in hard water. 3
Ans. Soap does not work well with hard water. This difficulty is overcome by using another kind of cleansing agent called detergents.
A detergent is the sodium salt of a long chain benzene sulphonic acid.
A common detergent is sodium n-dodecyl benzene sulphonate. Detergents can lather well even in hard water because they do not form insoluble calcium or magnesium salts on reacting with the calcium and magnesium ions present in hard water. A detergent works by making the oil and grease particles of dirty clothes dissolve in water through the formation of miscelles.
Q. 13. A student focussed the image of a candle flame on a white screen by placing the flame at various distances from a convex lens. He noted his observations in the following table:
Distance of the flame from the lens (cm) | Distance of the screen from the lens (cm) |
60 40 30 24 12 | 20 24 30 40 70 |
Analyse the above table and answer the following questions:
(a) What is the focal length of the convex lens?
(b) Which set of observations is incorrect and why?
(c) Draw a ray diagram to show the image formation for any correct set of observations. 3
(a) What is the focal length of the convex lens?
(b) Which set of observations is incorrect and why?
(c) Draw a ray diagram to show the image formation for any correct set of observations. 3
(a) Focal length of Convex lens = 15 cm.
(b) Case 5 is incorrect as per calculations.
(c) Ray diagram for Case 3 when the object is at 2F. See Q. 5, Case IV (L.A.T.), Chapter 10.
(b) Case 5 is incorrect as per calculations.
(c) Ray diagram for Case 3 when the object is at 2F. See Q. 5, Case IV (L.A.T.), Chapter 10.
Q. 14. (a) What is meant by a functional group in an organic compound?
Name the functional group present in
(i) CH3CH2OH (ii) CH3COOH
(b) State one point of difference between soap and synthetic detergent. 3
Name the functional group present in
(i) CH3CH2OH (ii) CH3COOH
(b) State one point of difference between soap and synthetic detergent. 3
Ans. (a) An ‘atom’ or ‘a group of atoms’ which makes a carbon compound reactive and decides its properties is called a functional group.
(i) CH3CH2OH → functional group is alcohol group: — OH
(ii) CH3COOH → functional group is carboxylic acid group: —COOH
(b) Soaps are biodegradable substances while detergents are nonbiodegradable substances.
(i) CH3CH2OH → functional group is alcohol group: — OH
(ii) CH3COOH → functional group is carboxylic acid group: —COOH
(b) Soaps are biodegradable substances while detergents are nonbiodegradable substances.
Q. 15. (a) What are ionic compounds? List any four physical properties of these compounds.
(b) What reaction happens when manganese dioxide is heated with aluminium powder? In which physical state is the metal produced in this reaction and why? 5
(b) What reaction happens when manganese dioxide is heated with aluminium powder? In which physical state is the metal produced in this reaction and why? 5
Ans. (a) The chemical bond formed by the transfer of electrons from one atom to another is known as an ionic bond and the compounds formed by such bonds are called ionic compounds.
Physical properties of ionic compounds:
1. Ionic compounds are usually crystalline solids because their oppositely charged ions attract one another strongly and form a regular crystal structure.
2. Ionic compounds have high melting points and high boiling points.
3. Ionic compounds are highly soluble in water.
4. Ionic compounds conduct electricity when dissolved in water or when melted because they contain charged particles i.e. ions.
1. Ionic compounds are usually crystalline solids because their oppositely charged ions attract one another strongly and form a regular crystal structure.
2. Ionic compounds have high melting points and high boiling points.
3. Ionic compounds are highly soluble in water.
4. Ionic compounds conduct electricity when dissolved in water or when melted because they contain charged particles i.e. ions.
(b) When manganese dioxide is heated with aluminium powder, manganese metal is produced
An alloy of mercury metal with one or more other metals is known as an amalgam. e.g., a solution of sodium metal in liquid mercury metal is called sodium amalgam.
(b) The most widely used method for refining impure metals is electrolytic refining.
(c) Labelled diagram to show the refining of copper
The reduction of manganese dioxide with aluminium is a highly exothermic reaction. A lot of heat is evolved therefore the manganese metal produced is in molten state.
Or
(a) What is an alloy? How does it differ from an amalgam?
(b) Name the method most widely used for refining impure metals.
(c) Draw a labelled diagram to show the refining of copper. 5
Ans. (a) An alloy is a homogeneous mixture of two or more metals (or a metal and small amounts of non-metals). The properties of an alloy are different from the properties of the constituent metals.(b) Name the method most widely used for refining impure metals.
(c) Draw a labelled diagram to show the refining of copper. 5
An alloy of mercury metal with one or more other metals is known as an amalgam. e.g., a solution of sodium metal in liquid mercury metal is called sodium amalgam.
(b) The most widely used method for refining impure metals is electrolytic refining.
(c) Labelled diagram to show the refining of copper
Q. 16. (a) State right hand thumb rule for finding the direction of magnetic field associated with a current carrying conductor. Draw a labelled diagram to show the experimental set-up for demonstrating the
rule. Mark the directions of the current and the associated magnetic field on the diagram.
rule. Mark the directions of the current and the associated magnetic field on the diagram.
(b) List two precautions which should be observed for the safety of the user and to avoid short circuiting in domestic circuits. 5
Ans. (a) Right hand thumb rule: See Q.3 (S.A.T.), Chapter 13. [Page 146 Diagram: See Q.14 (S.A.T.), Chapter 13. [Page 148
(b) Precautions which should be observed to avoid short circuiting in domestic circuits:
(i) Short circuiting can cause fires which can be highly damaging to electrical appliances and buildings. So, fuse of proper rating must be used to avoid such damages, as such a fuse-wire will melt before the temperature of the heated circuit wire gets too high and the circuit breaks.
(b) Precautions which should be observed to avoid short circuiting in domestic circuits:
(i) Short circuiting can cause fires which can be highly damaging to electrical appliances and buildings. So, fuse of proper rating must be used to avoid such damages, as such a fuse-wire will melt before the temperature of the heated circuit wire gets too high and the circuit breaks.
(ii) Old wiring should be checked regularly or changed when required.
Or
(a) What is a solenoid? Draw a labelled diagram to show the use of a current carrying solenoid to magnetise a steel rod. What is the nature of magnetic field lines inside a solenoid? What do these lines indicate?
(b) What is an electric fuse? What result do you expect if someone operates an electric heater of power rating 2 kW, 220 V in a domestic electric circuit (220 V) that has a fuse of current rating of 5 A? Justify your answer. 5
Ans. (a) A solenoid is a long coil containing a large number of close turns of insulated copper wire. The magnetic field produced by a current(b) What is an electric fuse? What result do you expect if someone operates an electric heater of power rating 2 kW, 220 V in a domestic electric circuit (220 V) that has a fuse of current rating of 5 A? Justify your answer. 5
carrying solenoid is similar to the magnetic field produced by a bar magnet. The magnetic field lines inside the solenoid are in the form of parallel straight lines. This indicates that the strength of magnetic field is the same at all points inside the solenoid. It is said to be a uniform magnetic field.
(b) An electric fuse is a safety device having a short length of a thin, tinplated copper wire having low melting point, which melts and breaks the circuit if the current exceeds a safe value. • Power of the electric heater,
Power of the electric heater,
P = 2 KW = 2 X 1000 W = 2000 W
Voltage, V = 220 V
P = 2 KW = 2 X 1000 W = 2000 W
Voltage, V = 220 V
An electric heater withdraws a 9·09 A current but the current rating of the fuse in the circuit is 5 A. Drawing a large quantity of current more than the capacity of fuse makes the fuse burn out. And thus a fuse in the circuit prevents damage to the appliance and the circuit due to overloading.
Section B
Q. 17. A young green plant receives sunlight from one direction only. What will happen to its shoots and roots? 1
Ans. (1) The roots bend away from light.
(2) The stem bends towards the light.
(2) The stem bends towards the light.
Q. 18. Name the plant hormones which help/promote
(i) cell division (ii) growth of the stem 1
(i) cell division (ii) growth of the stem 1
Ans. (i) Cytokinins help/promote cell devision.
(ii) Auxins help/promote growth of the stem.
(ii) Auxins help/promote growth of the stem.
Q. 19. Name any two forest products, each of which is the basis for some industry. 1
Ans. (i) Wood. It is used in timber industry, paper mills etc.
(ii) Latex of Rubber plant. It is used in various rubber industries like tyres etc.
(ii) Latex of Rubber plant. It is used in various rubber industries like tyres etc.
Q. 20. What is nuclear energy? State its one advantage. 2
Ans. The energy released during a nuclear reaction is called nuclear energy. The energy released is mainly in the form of heat. Advantage of nuclear energy. A small amount of mass of nucleus is destroyed during a controlled nuclear reaction which gets converted into a tremendous amount of energy to produce electricity.
Q. 21. Name the information source of making proteins in the cell. State two basic events in reproduction. 2
Ans. The information source of making proteins in cell is DNA.
Two basic events in reproduction are:
(i) The creation of a DNA copy. Here the cells use chemical reactions to build copies of their DNA. This creates two copies of the DNA in a reproducing cell.
(ii) DNA copying is accompanied by the creation of an additional cellular apparatus, and then the DNA copies separate, each with its own cellular apparatus. Effectively, a cell divides to give rise to two cells.
(i) The creation of a DNA copy. Here the cells use chemical reactions to build copies of their DNA. This creates two copies of the DNA in a reproducing cell.
(ii) DNA copying is accompanied by the creation of an additional cellular apparatus, and then the DNA copies separate, each with its own cellular apparatus. Effectively, a cell divides to give rise to two cells.
Q. 22. List four advantages of using solar cells. 2
Ans. Advantages of using solar cells:
(i) They have no moving parts.
(ii) They require almost no maintenance.
(iii) They work quite satisfactorily even without using any light focussing device.
(iv) They can be set up in remote, inaccessible and very sparsely inhabited areas where the laying of usual power transmission lines is difficult and expensive.
(i) They have no moving parts.
(ii) They require almost no maintenance.
(iii) They work quite satisfactorily even without using any light focussing device.
(iv) They can be set up in remote, inaccessible and very sparsely inhabited areas where the laying of usual power transmission lines is difficult and expensive.
Q. 23. Name the male and female gametes in animals. What is fertilization and where does it take place in human females? 2
Ans. In animals male gamete is called ‘sperm’ and the female gamete is called ‘ovum’ (or ‘ova’).
Fertilization. The fusion of a male gamete with a female gamete to form a zygote during sexual reproduction is called fertilization. The fertilization of the ovum (or egg) takes place in the oviduct.
Q. 24. How is ozone formed in the upper atmosphere? Why is the damage of ozone layer a cause of concern to us? State a cause of this damage. 2
Ans. Ozone is formed high up in the atmosphere by the action of ultraviolet radiation on oxygen gas by the following process:
Step 1. The high energy UV radiation running from the sun splits oxygen gas into free oxygen atoms
Step 1. The high energy UV radiation running from the sun splits oxygen gas into free oxygen atoms
Step 2. The free oxygen atoms thus produced are very reactive. One oxygen atom reacts with an oxygen molecule to form an ozone molecule.
This layer of ozone prevents the entry of harmful UV radiation to the earth’s surface, hence the damage to ozone layer is a cause of great concern to the mankind.
Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), which are used in refrigerants, deodrandts and in fire extinguishers, are one of the major causes of depletion of ozone layer.
Q. 25. What was “Chipko Movement”? How did this movement ultimately benefit the local population and the environment? 3
Ans. ‘Chipko Movement’: Chipko Movement is an example of contribution of common people towards the conservation of forests. The Chipko Movement [also called Hug the tree movement] originated from an incident in a remote village called ‘Reni’ in Garhwal (Himalayas), where the people of this village clasped the tree trunks with their arms to protect them from being cut down by a contractor’s workers. The people acted this way because they knew that this mass deforestation would spoil their healthy environment. The forest trees were thus saved. The Chipko Movement quickly spread across all the communities and hence helped in the conservation of forests and thus helped in safeguarding the environment
Q. 26. What is meant by exploitation of resources with short term aims? List its four advantages. 3
Ans. Exploitation of resources with short term aims means that management of natural resources is done in such a way so as to achieve short term gains which are enjoyed by just a handful of rich and powerful people. Resources are exploited to the hilt to meet the needs of the present generation without thinking of the needs of future generations.
Advantages:
(1) The main advantage of exploiting resources with short-term perspective is to get huge profit without any accountability.
(2) These resources fulfil the needs of present generation.
(3) Man gets a variety of raw materials from natural resources which are indispensable for the growth and development of our present day industries.
(4) It increases the (present day) growth rate of economy.
Advantages:
(1) The main advantage of exploiting resources with short-term perspective is to get huge profit without any accountability.
(2) These resources fulfil the needs of present generation.
(3) Man gets a variety of raw materials from natural resources which are indispensable for the growth and development of our present day industries.
(4) It increases the (present day) growth rate of economy.
Q. 27. (a) What is meant by breathing? What happens to the rate of breathing during vigorous exercise and why?
(b) Define translocation with respect to transport in plants. Why is it essential for plants? Where in plants are the following synthesised:
(i) Sugar (ii) Hormone 5
(b) Define translocation with respect to transport in plants. Why is it essential for plants? Where in plants are the following synthesised:
(i) Sugar (ii) Hormone 5
Ans. (a) Breathing. The mechanism by which organisms obtain oxygen from the air and release carbon dioxide is called breathing.
During vigorous exercise the demand of oxygen in the body tissues increases exponentially. Due to this, the rate of breathing increases during vigorous exercise.
(b) Translocation. The transport of food from the leaves to other parts of the plant is called translocation.
Leaves make food by the process of photosynthesis. The food made by leaves is in the form of simple sugar (glucose). Other type of substances called plant hormones are made in the tips of roots and
shoots. Every part of the plant needs food. So, food made in the leaves of a plant has to be transported (or carried) to all the different parts of the plant like branches, stem and roots etc.
(i) Sugar is synthesized in the leaves.
(ii) Hormones are synthesized in the tips of growing roots and shoots.
During vigorous exercise the demand of oxygen in the body tissues increases exponentially. Due to this, the rate of breathing increases during vigorous exercise.
(b) Translocation. The transport of food from the leaves to other parts of the plant is called translocation.
Leaves make food by the process of photosynthesis. The food made by leaves is in the form of simple sugar (glucose). Other type of substances called plant hormones are made in the tips of roots and
shoots. Every part of the plant needs food. So, food made in the leaves of a plant has to be transported (or carried) to all the different parts of the plant like branches, stem and roots etc.
(i) Sugar is synthesized in the leaves.
(ii) Hormones are synthesized in the tips of growing roots and shoots.
Or
Draw sectional view of the human heart and label on it the following chambers:
(i) Left atrium (ii) Right atrium (iii) Left ventricle (iv) Right ventricle State one function of each chamber in a tabular form. 5
(i) Left atrium (ii) Right atrium (iii) Left ventricle (iv) Right ventricle State one function of each chamber in a tabular form. 5
Ans. Diagram. See Q.27, Sample Paper II. [Page 19
Also add : (iv) Right ventricle—Send deoxygenated Blood to the lungs.
Also add : (iv) Right ventricle—Send deoxygenated Blood to the lungs.
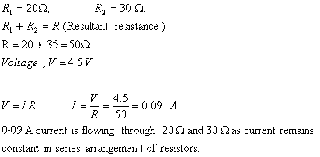







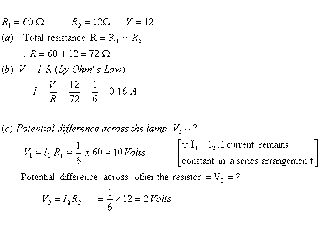



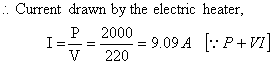


No comments:
Post a Comment