Comptt
Set- III - (Delhi)
Section A
Q. 1. Calcium, Strontium and Barium form a Dobereiner’s triad. The atomic masses of Calcium and Barium are 40 and 137 respectively. Predict the atomic mass of Strontium. 1
Ans.
Element of the triad Symbol Atomic masses
Calcium Ca 40
Strontium Sr ?
Barium Ba 137
According to Dobereiner’s triad, atomic mass of Strontium is the arithmetic mean of Ca and Ba.
Q. 2. Name the compound formed when ethanol is warmed with ethanoic acid in the presence of a few drops of conc. H2SO4. 1
Ans. When ethanol is warmed with ethanoic acid in the presence of a few drops of conc. H2SO4, a sweet smelling ester, ethyl ethanoate is formed.
Q. 3. Lithium, sodium and potassium form a Dobereiner’s triad. The atomic masses of lithium and potassium are 7 and 39 respectively. Predict the atomic mass of sodium. 1
Ans. The atomic mass of sodium is the arithmetic mean of the masses of lithium and potassium.
Q. 4. Redraw the diagram given in your answer book and show the direction of the light ray after reflection from the mirror. 1
Ans:
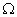 and 9
and 9 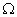 are connected in series to a battery of 3 V. How do the values of current passing through them compare?
are connected in series to a battery of 3 V. How do the values of current passing through them compare?Q. 6. Redraw the diagram given in your answer book and show the direction of the light ray after reflection from the mirror. 1
Ans. When an incident ray passes through the focus of a convex mirror the reflected ray will be parallel to the principal axis.
Q. 7. Describe an activity to observe what happens when quick lime is added to water taken in a beaker. State one important observation and name the type of reaction taking place. 2
Ans. Activity:
(i) Small amount of water is taken in a beaker.
(ii) A little amount of quicklime is added slowly to the beaker.
(iii) When we touch the beaker carefully, the beaker feels to be quite hot. Therefore the chemical reaction between quicklime and water to form slaked lime is characterised by a change in temperature i.e. rise in temperature.
Thus the reaction between quicklime and water is an exothermic reaction (i.e. heat producing reaction).
(i) Small amount of water is taken in a beaker.
(ii) A little amount of quicklime is added slowly to the beaker.
(iii) When we touch the beaker carefully, the beaker feels to be quite hot. Therefore the chemical reaction between quicklime and water to form slaked lime is characterised by a change in temperature i.e. rise in temperature.
Thus the reaction between quicklime and water is an exothermic reaction (i.e. heat producing reaction).
Q. 8. State two main properties of elements on which Mendeleev’s periodic classification was based. Why could no fixed position be assigned to hydrogen in his periodic table? 2
Ans. The two main properties of elements on which Mendeleev’s periodic classification was based:
(i) on the basis of the reaction of elements with hydrogen.
(ii) on the basis of the reaction of elements with oxygen.
No fixed position was given to hydrogen in Mendeleev’s periodic table because electronic configuration of hydrogen resembles that of alkali metals. So like alkali metals, hydrogen also combines with halogens,
oxygen and sulphur to form compounds having similar formulae.
(i) on the basis of the reaction of elements with hydrogen.
(ii) on the basis of the reaction of elements with oxygen.
No fixed position was given to hydrogen in Mendeleev’s periodic table because electronic configuration of hydrogen resembles that of alkali metals. So like alkali metals, hydrogen also combines with halogens,
oxygen and sulphur to form compounds having similar formulae.
Compounds of H | Compounds of Na |
HCI | NaCI |
H2O | Na2O |
H2S | Na2S |
On the other hand, just like halogens, hydrogen also exists as diatomic molecules and it combines with metals and non-metals to form covalent compounds.
Q. 9. What is dispersion of light? Name the (i) component of white light that deviates the least and (ii) the component that deviates the most while passing through a glass prism. 2
Ans. The splitting up of white light into seven colours on passing through a transparent medium like a glass prism is called dispersion of light. When white light passes through the glass prism:
(i) The red component of the white light is deviated least.
(ii) The violet component of the white light is deviated the most.
(i) The red component of the white light is deviated least.
(ii) The violet component of the white light is deviated the most.
Q. 10. Why does the sky look blue on a clear sunny day? Explain. 2
Ans. See Q.18 (S.A.T), Chapter 11.
Q. 11. State the name and function of the acid produced in our stomach. What remedy would you suggest to a person suffering from indigestion, pain and irritation in the stomach? Name the main ingredient of this remedy and state its function. 3
Ans. Our stomach produces hydrochloric acid. This dilute hydrochloric acid helps in digesting our food without harming the stomach. Sometimes excess acid is produced in the stomach due to various reasons like overeating. The excess acid in the stomach causes indigestion which produces pain and irritation. In order to cure indigestion, antacids are given.
Antacids are a group of mild bases which have no toxic effects on the body. As antacids are basic in nature so they neutralise the excess acid of the stomach and give relief to the person.
The two common antacids used for curing indigestion due to acidity are :
Magnesium hydroxide (milk of magnesia) and Sodium hydrogen carbonate (baking soda).
. 12. Draw a circuit diagram to show an electric lamp of resistance 42 Antacids are a group of mild bases which have no toxic effects on the body. As antacids are basic in nature so they neutralise the excess acid of the stomach and give relief to the person.
The two common antacids used for curing indigestion due to acidity are :
Magnesium hydroxide (milk of magnesia) and Sodium hydrogen carbonate (baking soda).
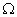 and a resistor of 18
and a resistor of 18 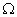 connected in series with a battery of 6 V. Calculate
connected in series with a battery of 6 V. Calculate (a) total resistance in the circuit
(b) current flowing through the circuit
(c) potential difference separately across the lamp and the resistor. 3
Ans. (a) Total resistance in the circuit, R = ?
R = R1 + R2 = 42 + 18 = 60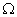 R1 = 42
R1 = 42 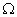 R2 = 18
R2 = 18 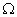
b) Current flowing through the circuit, I = ?
Potential difference, V = 6 volts
According to Ohm’s law
R = R1 + R2 = 42 + 18 = 60
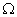 R1 = 42
R1 = 42 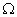 R2 = 18
R2 = 18 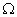
b) Current flowing through the circuit, I = ?
Potential difference, V = 6 volts
According to Ohm’s law
Q. 13. (a) What are salts among chemical substances? Give an example of a salt derived from a strong acid and a weak base. State the behaviour of aqueous solution of this salt towards litmus solution.
(b) Why does hydrogen chloride gas not show acidic behaviour? 3
(b) Why does hydrogen chloride gas not show acidic behaviour? 3
Ans. (a) A salt is a compound formed by the reaction between an acid and a base. Ammonium chloride (NH4Cl) is a salt of a strong acid, hydrochloric.acid (HCl), and a weak base, ammonium hydroxide (NH4OH). This salt is acidic in nature therefore it turns blue litmus red.
(b) The acidic behaviour of acids is due to the presence of hydrogen ions, H+ (aq) ions in them. The acids produce hydrogen ions only in the presence of water. So, in the absence of water, a substance will not form hydrogen ions and hence will not show its acidic behaviour. So HCl gas does not show acidic behaviour.
Q. 14. Draw a circuit diagram to show an electric lamp of resistance 30 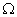 and a resistor of 6
and a resistor of 6 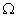 connected in series with a battery of 6 V. Calculate
connected in series with a battery of 6 V. Calculate
(a) total resistance in the circuit
(b) current flowing through the circuit
(c) potential difference separately across the lamp and the resistor. 3
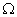 and a resistor of 6
and a resistor of 6 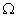 connected in series with a battery of 6 V. Calculate
connected in series with a battery of 6 V. Calculate(a) total resistance in the circuit
(b) current flowing through the circuit
(c) potential difference separately across the lamp and the resistor. 3
Soln:
Q. 15. (a) What are ionic compounds? List any four physical properties of these compounds.
(b) What reaction happens when manganese dioxide is heated with aluminium powder? In which physical state is the metal produced in this reaction and why? 5
(b) What reaction happens when manganese dioxide is heated with aluminium powder? In which physical state is the metal produced in this reaction and why? 5
Ans. (a) The chemical bond formed by the transfer of electrons from one atom to another is known as an ionic bond and the compounds formed by such bonds are called ionic compounds.
Physical properties of ionic compounds:
1. Ionic compounds are usually crystalline solids because their oppositely charged ions attract one another strongly and form a regular crystal structure.
2. Ionic compounds have high melting points and high boiling points.
3. Ionic compounds are highly soluble in water.
4. Ionic compounds conduct electricity when dissolved in water or when melted because they contain charged particles i.e. ions.
1. Ionic compounds are usually crystalline solids because their oppositely charged ions attract one another strongly and form a regular crystal structure.
2. Ionic compounds have high melting points and high boiling points.
3. Ionic compounds are highly soluble in water.
4. Ionic compounds conduct electricity when dissolved in water or when melted because they contain charged particles i.e. ions.
(b) When manganese dioxide is heated with aluminium powder, manganese metal is produced
Q. 15. (a) What are ionic compounds? List any four physical properties of these compounds.
(b) What reaction happens when manganese dioxide is heated with aluminium powder? In which physical state is the metal produced in this reaction and why? 5
(b) What reaction happens when manganese dioxide is heated with aluminium powder? In which physical state is the metal produced in this reaction and why? 5
Ans. (a) The chemical bond formed by the transfer of electrons from one atom to another is known as an ionic bond and the compounds formed by such bonds are called ionic compounds.
Physical properties of ionic compounds:
1. Ionic compounds are usually crystalline solids because their oppositely charged ions attract one another strongly and form a regular crystal structure.
2. Ionic compounds have high melting points and high boiling points.
3. Ionic compounds are highly soluble in water.
4. Ionic compounds conduct electricity when dissolved in water or when melted because they contain charged particles i.e. ions.
1. Ionic compounds are usually crystalline solids because their oppositely charged ions attract one another strongly and form a regular crystal structure.
2. Ionic compounds have high melting points and high boiling points.
3. Ionic compounds are highly soluble in water.
4. Ionic compounds conduct electricity when dissolved in water or when melted because they contain charged particles i.e. ions.
(b) When manganese dioxide is heated with aluminium powder, manganese metal is produced
Q. 15. (a) What are ionic compounds? List any four physical properties of these compounds.
(b) What reaction happens when manganese dioxide is heated with aluminium powder? In which physical state is the metal produced in this reaction and why? 5
(b) What reaction happens when manganese dioxide is heated with aluminium powder? In which physical state is the metal produced in this reaction and why? 5
Ans. (a) The chemical bond formed by the transfer of electrons from one atom to another is known as an ionic bond and the compounds formed by such bonds are called ionic compounds.
Physical properties of ionic compounds:
1. Ionic compounds are usually crystalline solids because their oppositely charged ions attract one another strongly and form a regular crystal structure.
2. Ionic compounds have high melting points and high boiling points.
3. Ionic compounds are highly soluble in water.
4. Ionic compounds conduct electricity when dissolved in water or when melted because they contain charged particles i.e. ions.
1. Ionic compounds are usually crystalline solids because their oppositely charged ions attract one another strongly and form a regular crystal structure.
2. Ionic compounds have high melting points and high boiling points.
3. Ionic compounds are highly soluble in water.
4. Ionic compounds conduct electricity when dissolved in water or when melted because they contain charged particles i.e. ions.
(b) When manganese dioxide is heated with aluminium powder, manganese metal is produced
An alloy of mercury metal with one or more other metals is known as an amalgam. e.g., a solution of sodium metal in liquid mercury metal is called sodium amalgam.
(b) The most widely used method for refining impure metals is electrolytic refining.
(c) Labelled diagram to show the refining of copper
The reduction of manganese dioxide with aluminium is a highly exothermic reaction. A lot of heat is evolved therefore the manganese metal produced is in molten state.
Or
(a) What is an alloy? How does it differ from an amalgam?
(b) Name the method most widely used for refining impure metals.
(c) Draw a labelled diagram to show the refining of copper. 5
Ans. (a) An alloy is a homogeneous mixture of two or more metals (or a metal and small amounts of non-metals). The properties of an alloy are different from the properties of the constituent metals.(b) Name the method most widely used for refining impure metals.
(c) Draw a labelled diagram to show the refining of copper. 5
An alloy of mercury metal with one or more other metals is known as an amalgam. e.g., a solution of sodium metal in liquid mercury metal is called sodium amalgam.
(b) The most widely used method for refining impure metals is electrolytic refining.
(c) Labelled diagram to show the refining of copper
Q. 16. (a) State right hand thumb rule for finding the direction of magnetic field associated with a current carrying conductor. Draw a labelled diagram to show the experimental set-up for demonstrating the
rule. Mark the directions of the current and the associated magnetic field on the diagram.
rule. Mark the directions of the current and the associated magnetic field on the diagram.
(b) List two precautions which should be observed for the safety of the user and to avoid short circuiting in domestic circuits. 5
Ans. (a) Right hand thumb rule: See Q.3 (S.A.T.), Chapter 13. [Page 146 Diagram: See Q.14 (S.A.T.), Chapter 13. [Page 148
(b) Precautions which should be observed to avoid short circuiting in domestic circuits:
(i) Short circuiting can cause fires which can be highly damaging to electrical appliances and buildings. So, fuse of proper rating must be used to avoid such damages, as such a fuse-wire will melt before the temperature of the heated circuit wire gets too high and the circuit breaks.
(b) Precautions which should be observed to avoid short circuiting in domestic circuits:
(i) Short circuiting can cause fires which can be highly damaging to electrical appliances and buildings. So, fuse of proper rating must be used to avoid such damages, as such a fuse-wire will melt before the temperature of the heated circuit wire gets too high and the circuit breaks.
(ii) Old wiring should be checked regularly or changed when required.
Or
(a) What is a solenoid? Draw a labelled diagram to show the use of a current carrying solenoid to magnetise a steel rod. What is the nature of magnetic field lines inside a solenoid? What do these lines indicate?
(b) What is an electric fuse? What result do you expect if someone operates an electric heater of power rating 2 kW, 220 V in a domestic electric circuit (220 V) that has a fuse of current rating of 5 A? Justify your answer. 5
Ans. (a) A solenoid is a long coil containing a large number of close turns of insulated copper wire. The magnetic field produced by a current(b) What is an electric fuse? What result do you expect if someone operates an electric heater of power rating 2 kW, 220 V in a domestic electric circuit (220 V) that has a fuse of current rating of 5 A? Justify your answer. 5
carrying solenoid is similar to the magnetic field produced by a bar magnet. The magnetic field lines inside the solenoid are in the form of parallel straight lines. This indicates that the strength of magnetic field is the same at all points inside the solenoid. It is said to be a uniform magnetic field.
(b) An electric fuse is a safety device having a short length of a thin, tinplated copper wire having low melting point, which melts and breaks the circuit if the current exceeds a safe value. • Power of the electric heater,
Power of the electric heater,
P = 2 KW = 2 X 1000 W = 2000 W
Voltage, V = 220 V
P = 2 KW = 2 X 1000 W = 2000 W
Voltage, V = 220 V
Section B
Q. 17. Name any two types of asexual reproduction. 1
Ans. Fission and Budding.
Q. 18. State an instance where human intervention saved the forests from destruction. 1
Ans. ‘The Chipko Andolan’ is an example of the contribution of common people towards the conservation of forests. The Andolan originated from a remote village ‘Reni’ in Garhwal in the early 1970s in which villagers clasped the tree trunks with their arms to prevent them from being cut down.
Q. 19. What are the two kinds of natural resources? 1
Ans. Two kinds of natural resources are:
(1) Renewable
(2) Non-Renewable.
(1) Renewable
(2) Non-Renewable.
Q. 20. You have two solar cookers, one covered by a plane transparent glass sheet and the other kept open. Which of the two solar cookers will be more efficient and why? 2
Ans. The solar cooker covered by a plane transparent glass sheet is more effective than the solar cooker which is kept open. This is because once the sun’s heat rays enter the cooker box which is covered, the heat rays get trapped in the box due to which the temperature in the solar cooker rises considerably.
Q. 21. Name the information source of making proteins in the cell. State two basic events in reproduction. 2
Ans. The information source of making proteins in cell is DNA.
Two basic events in reproduction are:
(i) The creation of a DNA copy. Here the cells use chemical reactions to build copies of their DNA. This creates two copies of the DNA in a reproducing cell.
(ii) DNA copying is accompanied by the creation of an additional cellular apparatus, and then the DNA copies separate, each with its own cellular apparatus. Effectively, a cell divides to give rise to two cells.
(i) The creation of a DNA copy. Here the cells use chemical reactions to build copies of their DNA. This creates two copies of the DNA in a reproducing cell.
(ii) DNA copying is accompanied by the creation of an additional cellular apparatus, and then the DNA copies separate, each with its own cellular apparatus. Effectively, a cell divides to give rise to two cells.
Q. 22. List four advantages of using solar cells. 2
Ans. Advantages of using solar cells:
(i) They have no moving parts.
(ii) They require almost no maintenance.
(iii) They work quite satisfactorily even without using any light focussing device.
(iv) They can be set up in remote, inaccessible and very sparsely inhabited areas where the laying of usual power transmission lines is difficult and expensive.
(i) They have no moving parts.
(ii) They require almost no maintenance.
(iii) They work quite satisfactorily even without using any light focussing device.
(iv) They can be set up in remote, inaccessible and very sparsely inhabited areas where the laying of usual power transmission lines is difficult and expensive.
Q. 23. Name the major component of biogas. List two main advantages of using biogas over fossil fuels. 2
Ans. The major constituent of biogas is methane.
Advantages of biogas over fossil fuels:
(i) Biogas burns without smoke and hence does not cause air pollution.
(ii) Biogas burns completely without leaving behind any residue. So, it is a clean fuel.
Advantages of biogas over fossil fuels:
(i) Biogas burns without smoke and hence does not cause air pollution.
(ii) Biogas burns completely without leaving behind any residue. So, it is a clean fuel.
Q. 24. How is ozone formed in the upper atmosphere? Why is the damage of ozone layer a cause of concern to us? State a cause of this damage. 2
Ans. Ozone is formed high up in the atmosphere by the action of ultraviolet radiation on oxygen gas by the following process:Step 1. The high energy UV radiation running from the sun splits oxygen gas into free oxygen atoms
This layer of ozone prevents the entry of harmful UV radiation to the earth’s surface, hence the damage to ozone layer is a cause of great concern to the mankind.
Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), which are used in refrigerants, deodrandts and in fire extinguishers, are one of the major causes of depletion of ozone layer.
Q. 25. What is a dam? Write two main advantages and two ill-effects of constructing a big dam. 3
Ans. In order to make proper use of river water, dams are constructed across the rivers to regulate the flow of water. A dam has a large reservoir to store huge amount of water. This stored water is then allowed to flow downstream at the desired rate.
Advantages:
(i) Water from a dam is used for irrigation in fields through a network of canals. Dams ensure round the year water supply to the crop fields and help raise agricultural production.
(ii) The water rushing down the dam turns turbines which run electric generators to generate electricity.
(i) Water from a dam is used for irrigation in fields through a network of canals. Dams ensure round the year water supply to the crop fields and help raise agricultural production.
(ii) The water rushing down the dam turns turbines which run electric generators to generate electricity.
Ill-effects:
(i) Social problems because they displace large number of peasants and tribals without adequate compensation or rehabilitation.
(ii) Economic problems because they swallow up huge amounts of public money without the generation of proportionate benefits.
(i) Social problems because they displace large number of peasants and tribals without adequate compensation or rehabilitation.
(ii) Economic problems because they swallow up huge amounts of public money without the generation of proportionate benefits.
Q. 26. What is meant by exploitation of resources with short term aims? List its four advantages. 3
Ans. Exploitation of resources with short term aims means that management of natural resources is done in such a way so as to achieve short term gains which are enjoyed by just a handful of rich and powerful people. Resources are exploited to the hilt to meet the needs of the present generation without thinking of the needs of future generations.
Advantages:
(1) The main advantage of exploiting resources with short-term perspective is to get huge profit without any accountability.
(2) These resources fulfil the needs of present generation.
(3) Man gets a variety of raw materials from natural resources which are indispensable for the growth and development of our present day industries.
(4) It increases the (present day) growth rate of economy.
Advantages:
(1) The main advantage of exploiting resources with short-term perspective is to get huge profit without any accountability.
(2) These resources fulfil the needs of present generation.
(3) Man gets a variety of raw materials from natural resources which are indispensable for the growth and development of our present day industries.
(4) It increases the (present day) growth rate of economy.
Q. 27. (a) What is meant by breathing? What happens to the rate of breathing during vigorous exercise and why?
(b) Define translocation with respect to transport in plants. Why is it essential for plants? Where in plants are the following synthesised:
(i) Sugar (ii) Hormone 5
(b) Define translocation with respect to transport in plants. Why is it essential for plants? Where in plants are the following synthesised:
(i) Sugar (ii) Hormone 5
Ans. (a) Breathing. The mechanism by which organisms obtain oxygen from the air and release carbon dioxide is called breathing.
During vigorous exercise the demand of oxygen in the body tissues increases exponentially. Due to this, the rate of breathing increases during vigorous exercise.
(b) Translocation. The transport of food from the leaves to other parts of the plant is called translocation.
Leaves make food by the process of photosynthesis. The food made by leaves is in the form of simple sugar (glucose). Other type of substances called plant hormones are made in the tips of roots and
shoots. Every part of the plant needs food. So, food made in the leaves of a plant has to be transported (or carried) to all the different parts of the plant like branches, stem and roots etc.
(i) Sugar is synthesized in the leaves.
(ii) Hormones are synthesized in the tips of growing roots and shoots.
During vigorous exercise the demand of oxygen in the body tissues increases exponentially. Due to this, the rate of breathing increases during vigorous exercise.
(b) Translocation. The transport of food from the leaves to other parts of the plant is called translocation.
Leaves make food by the process of photosynthesis. The food made by leaves is in the form of simple sugar (glucose). Other type of substances called plant hormones are made in the tips of roots and
shoots. Every part of the plant needs food. So, food made in the leaves of a plant has to be transported (or carried) to all the different parts of the plant like branches, stem and roots etc.
(i) Sugar is synthesized in the leaves.
(ii) Hormones are synthesized in the tips of growing roots and shoots.
Or
Draw sectional view of the human heart and label on it the following chambers:
(i) Left atrium (ii) Right atrium (iii) Left ventricle (iv) Right ventricle State one function of each chamber in a tabular form. 5
(i) Left atrium (ii) Right atrium (iii) Left ventricle (iv) Right ventricle State one function of each chamber in a tabular form. 5
Ans. Diagram. See Q.27, Sample Paper II. [Page 19
Also add : (iv) Right ventricle—Send deoxygenated Blood to the lungs.
Also add : (iv) Right ventricle—Send deoxygenated Blood to the lungs.

















No comments:
Post a Comment